Reseach Interests and Current ProjectsMy primary research interest is genetic and epigenetic regulation of gene expression in vertebrates and insects. The main focus is allele-specific expression (ASE), allele-specific DNA methylation (ASM) and allele-specific histone modifications. Using comparative, evolutionary and functional genomic approaches, I profiled genome-wide allelic imbalance in a number of mammalian, non-mammal vertebrate and insect species. Specifically, I am investigating genomic imprinting, X chromosome inactivation, cis-/trans- regulation in gene expression, and DNA methylome evolution.
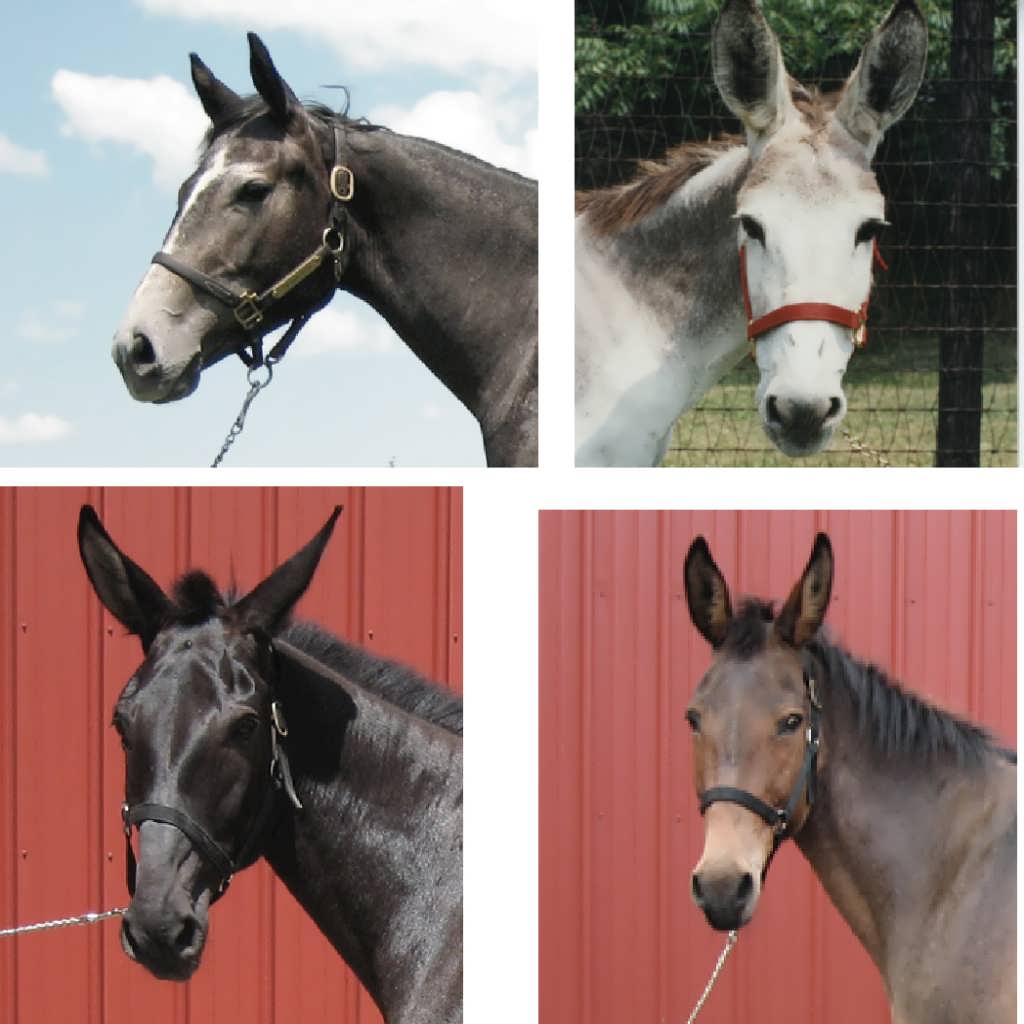
To estimate allele-specific expression and detect allelic imbalance, I used RNA-seq experiments in reciprocal F1 samples of inbred strains/species. The advantage of this design is to have every single SNP in the F1 transcripts be informative with trackable transmission direction. Allele-specific expression ratio could be estimated from the relative counts of the two parental alleles. I have been applying this pipeline in several organisms, including inbred mouse strains, horse and donkey (known as mule and hinny), cow and bison, two opossum lines, two inbred chicken breeds (Leghorn and Fayoumi), African and European bee and two jewel wasp species (Nasonia vitripennis and Nasonia giraulti). The ultimate goal is to understand the mechanism, origin and evolution of different forms of differential allelic expression.
|
|
|